Introduction
FuriosaAI NPU (Neural Processing Unit) has APIs available in C/C++ and Python for executing DNN models.
This document includes the FuriosaAI NPU FPGA installation guide, Jupyter Notebook examples, and compiler CLI usage instructions.
It also introduces the Nux Quantizer tool and APIs (again available in C/C++ and Python), which helps users quantize their models.
Prerequisites
- Linux (Ubuntu 18.04 LTS or later)
Installing FuriosaAI SDK
FPGA SDK Installation
Furiosa FPGA SDK can be installed on FPGA and AWS F1 instance in the link below.
Jupyter Notebook Examples
The demo Jupyter Notebook in the link below can be used to confirm how to models are compiled via the FuriosaAI NPU.
FuriosaAI Jupyter Notebook Examples
FuriosaAI CLI Usage
The Compiler CLI can be used in the link below.
Getting Started
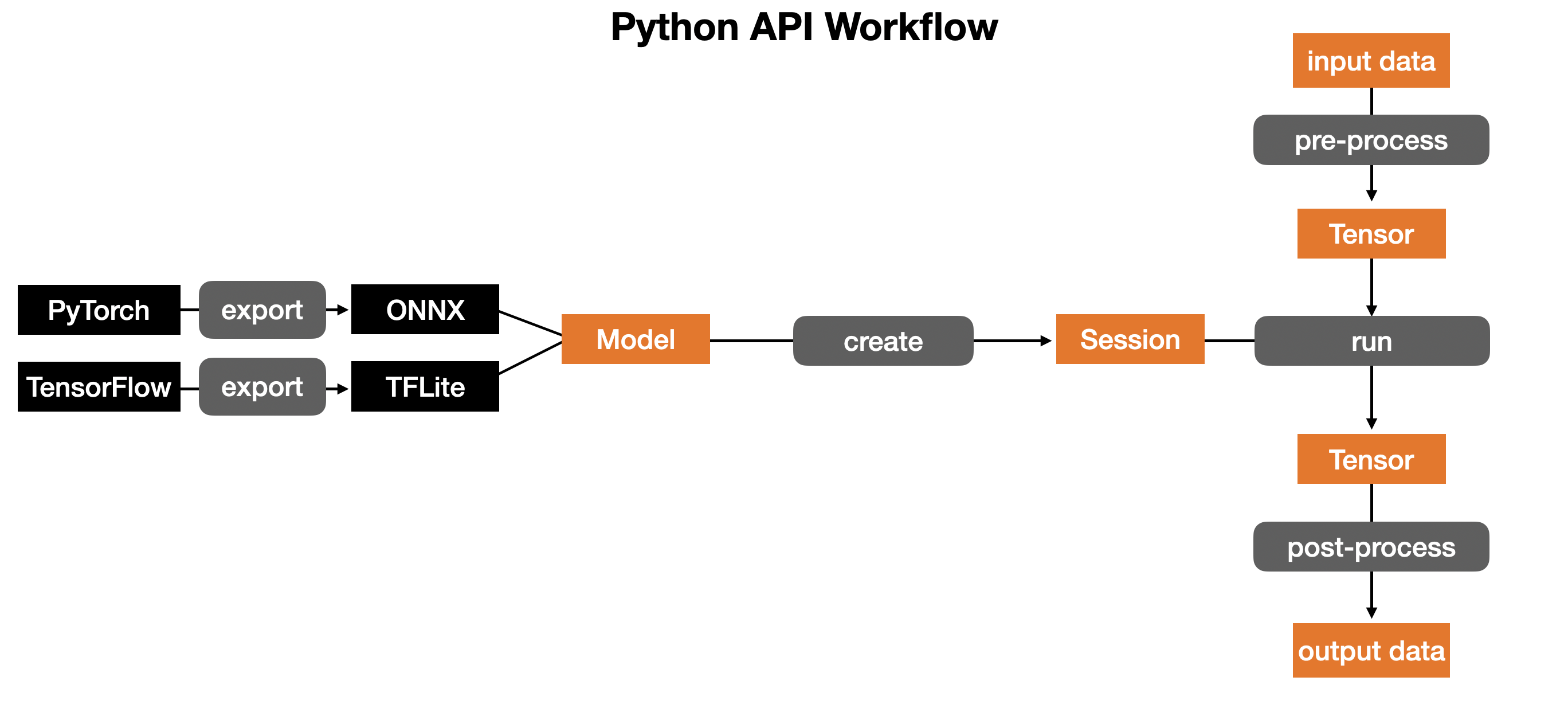 Python API workflow is as above.
Python API workflow is as above.
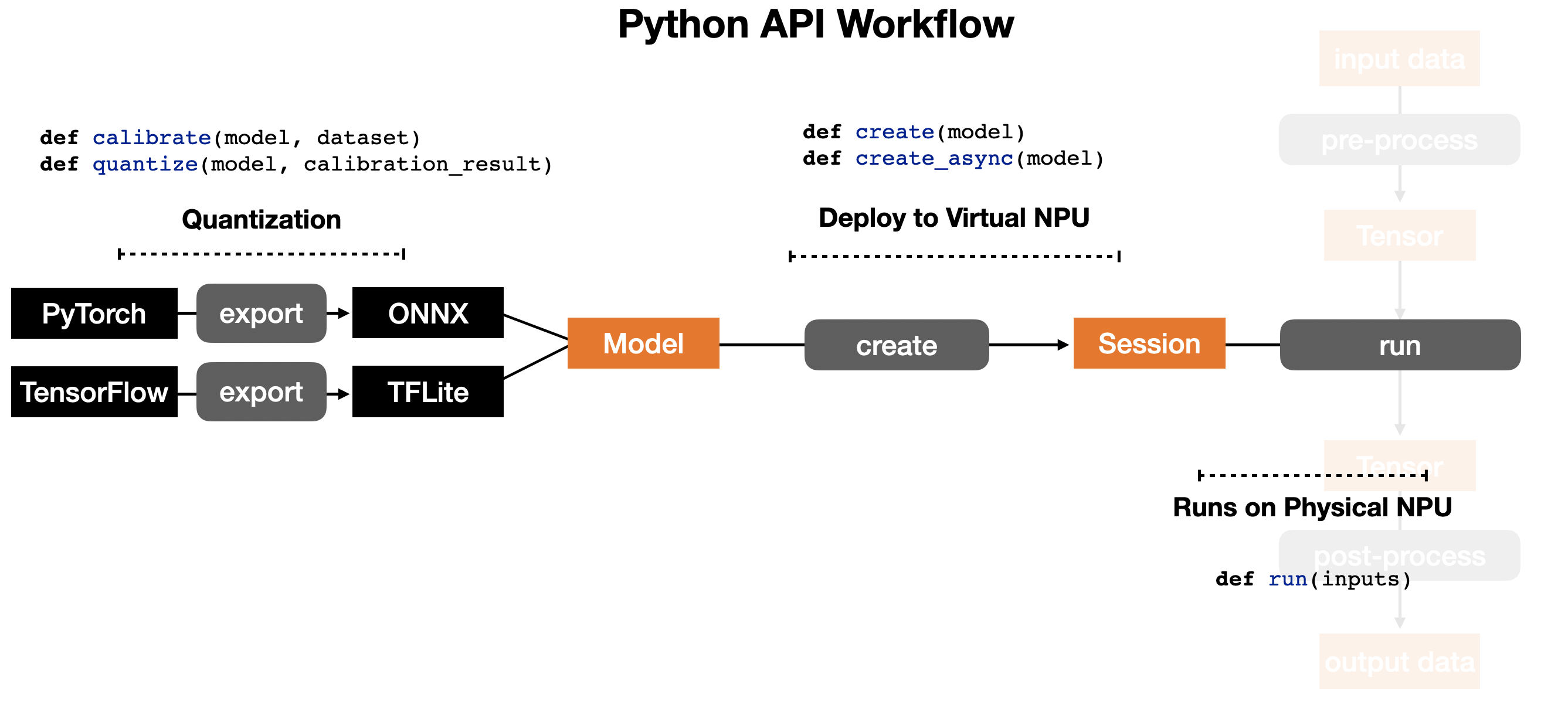 As modeled above, the porcess of running models on the NPU consists of the following three steps:
As modeled above, the porcess of running models on the NPU consists of the following three steps:
- To be usable by the Furiosa compiler, TensorFlow or Pytorch models need to be converted to either TFLite or ONNX models for Quantization.
- Compile the TFLite/ONNX model and deploy the compiled model to virtual NPU
- Run the compiled model on physical NPU
Nux Quantizer
The Nux-quantizer supports post-training 8-bit quantization.
The Nux-quantizer's quantization specification follows Tensorflow Lite 8-bit quantization specification.
The Nux-quantizer currently supports ONNX models, TensorFlow model support is slated for later in the SDK release schedule.
Quantization Getting Started
nux.quantizer.post_training_quantization()
One click quantization
import nux
model = ...
input_tensors = ...
calibration_data = ...
quantized_model = nux.quantizer.post_training_quantization(model, input_tensors, calibration_data)
with nux.session.create(quantized_model) as sess:
# ...
The input ONNX model can be quantized immediately with one-click. This function applies the following quantization schemes:
- To minimize accuracy drop from quantization,
convolutionoperators are quantizedper-channeland the other operators are quantizedper-tensor. - For faster inference than floating-point calculation, integer-only-arithmetic is applied using
staticquantization, which quantizes both weights and activation values.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| model | onnx.ModelProto ONNX model (ONNX format DNN model) |
| input_tensors | List[str] The names of the input tensors of the ONNX model |
| calibration_data | Union[Dict[str, np.ndarray], List[Dict[str, np.ndarray]]] Required calibration data for collecting a dynamic range of activations, randomly generated if not provided. |
Return
onnx.ModelProto static per-channel int8 quantized model
An Example of Exporting a Pytorch model to an ONNX model
The nux.quantizer.post_training_quantization function requires a ONNX model to be provided. The torch.onnx.export function exports a Pytorch model into ONNX model form.
The Example Python script converts the ExampleNet Pytorch model to an ONNX model and quantizes the ONNX model with a dynamic range collected with randomly generated calibration data.
Export Pytorch to ONNX
import io
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import onnx
import numpy as np
import nux
# describe Example Pytorch model
class ExampleNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(ExampleNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 3)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(6)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 12, 3)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(12)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(12, 3, 3)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
x = self.conv3(x)
return x
# util function for exporting Pytorch model to ONNX
def export_example_net():
dummy_input = torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)
input_names = ["input"]
output_names = ["output"]
model_io = io.BytesIO()
torch.onnx.export(ExampleNet(),
(dummy_input,),
model_io,
verbose=False,
input_names=input_names,
output_names=output_names)
model_io.seek(0)
return onnx.load_model(model_io)
# util function to get input tensor name
def example_net_input_tensors():
return ["input"]
model = export_example_net()
quantized_model = nux.quantizer.post_training_quantization(model, example_net_input_tensors())
with nux.session.create(quantized_model) as sess:
# ...
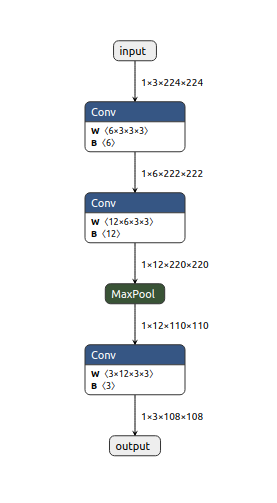
The ONNX model ExampleNet is visualized by Netron as follows:
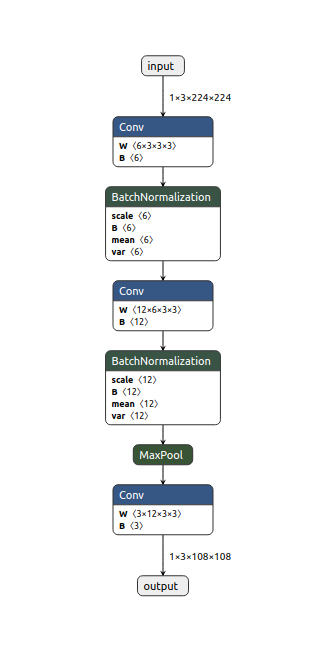
Nux Quantizer in detail
Nux Quantizer in detail
import nux
IS_TEST = ...
input_tensors = example_net_input_tensors()
model = export_example_net()
# graph optimization
optimized_model = nux.quantizer.optimize(model)
# calibration
calibration_model = nux.quantizer.build_calibration_model(optimized_model, input_tensors)
if IS_TSET:
dynamic_ranges = nux.quantizer.calibrate_with_random_input(calibration_model)
else:
calibration_data = get_calibration_data(...)
dynamic_ranges = nux.quantizer.calibrate(calibration_model, calibration_data)
# quantization
quantized_model = nux.quantizer.quantize(optimized_model, input_tensors, dynamic_ranges)
with nux.session.create(quantized_model) as sess:
# ...
The workflow of nux-quantizer is as according to the diagram below: An input ONNX model goes through 1) graph optimization 2) calibration 3) quantization to output a quantized ONNX model.
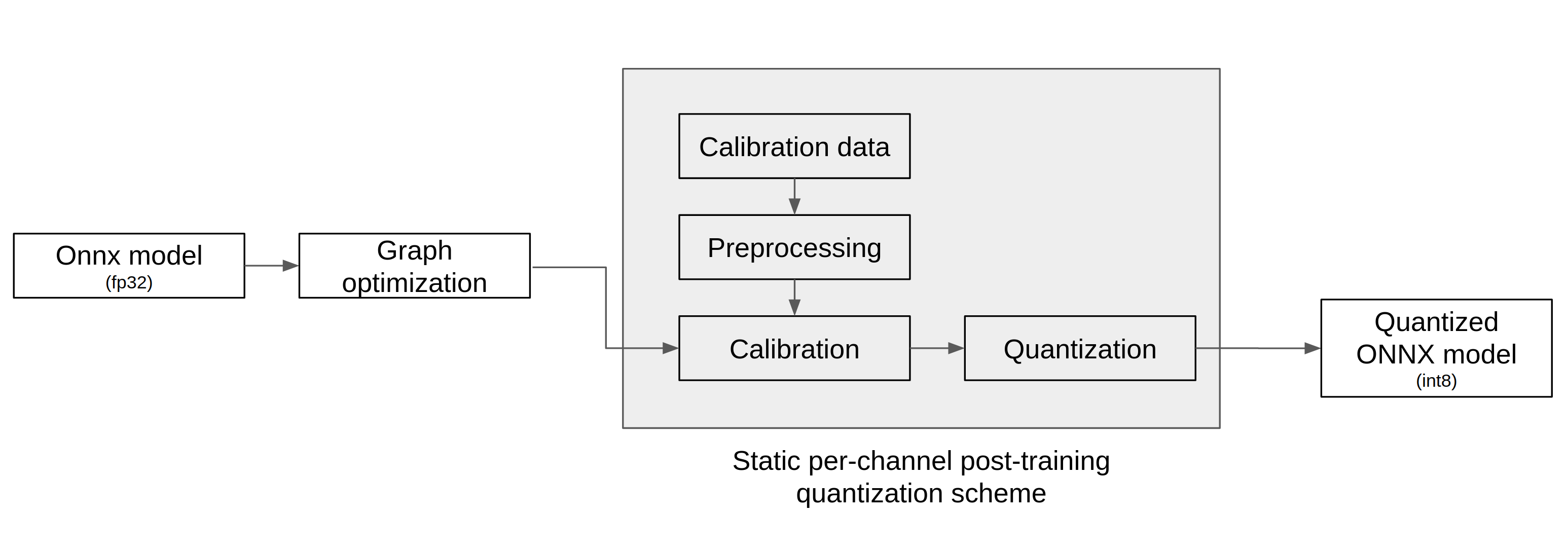
Graph Optimization
Graph Optimization
import nux
model = ...
optimized_model = nux.quantizer.optimize(model)
nux.quantizer.optimize()
This function prepares an ONNX model for calibration and quantization by optimizing it. The input ONNX model is optimized by graph optimization techniques such as tensor shape inference for each node's output, operator fusion, etc.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| model | onnx.ModelProto ONNX model |
Return
onnx.ModelProto Optimized ONNX model
Result
The output of the ONNX model optimization, the optimized ExampleNet is displayed below:
Calibration
nux.quantizer.build_calibration_model()
Calibration
import nux
IS_TEST = ...
optimized_model = ...
input_tensors = ...
calibration_model = nux.quantizer.build_calibration_model(optimized_model, input_tensors)
if not IS_TSET:
calibration_data = get_calibration_data(...) # user-written function
dynamic_ranges = nux.quantizer.calibrate(calibration_model, calibration_data)
else:
dynamic_ranges = nux.quantizer.calibrate_with_random_input(calibration_model)
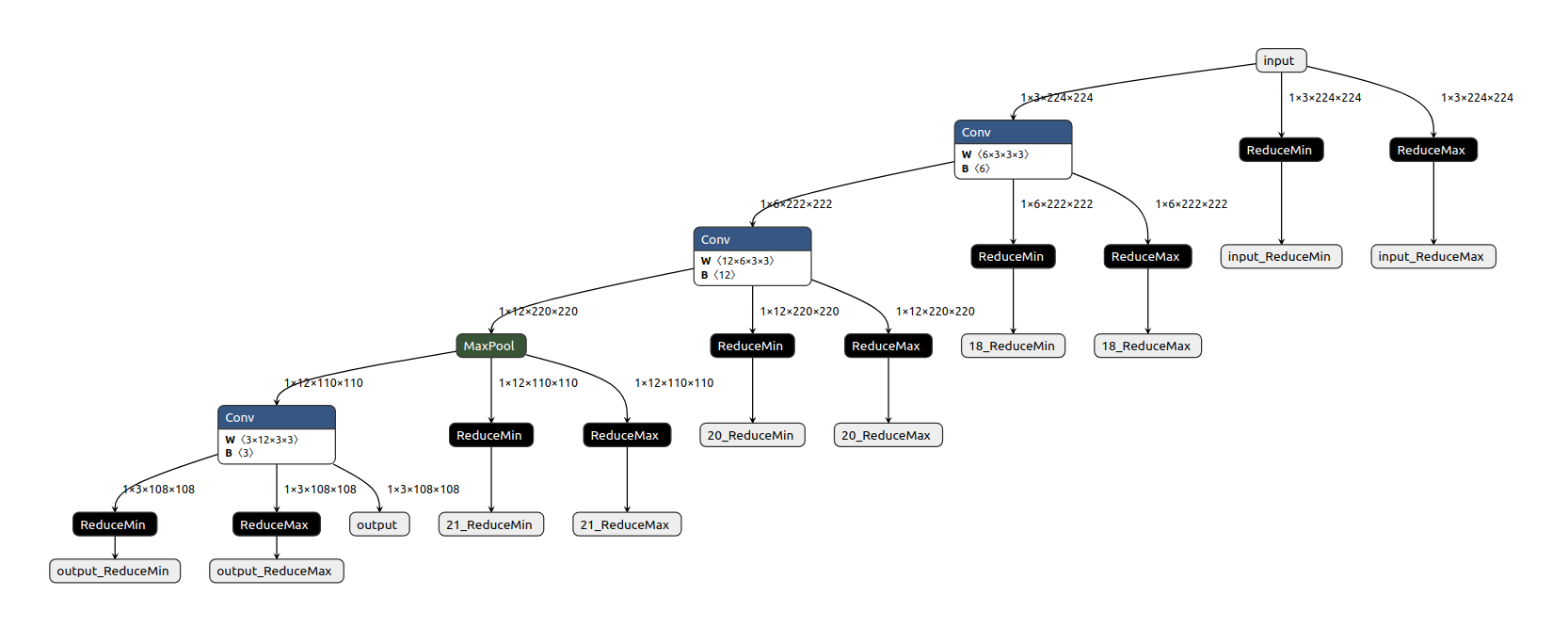
This function prepares the ONNX model for static quantization by adding ReduceMin and ReduceMax nodes to every output node.
This creates a model for calibrating the dynamic range of activation values from the given calibration data.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| model | onnx.ModelProto ONNX model |
| input_tensors | List[str] Names of the ONNX model's input tensors |
Return
onnx.ModelProto Calibration model
Result
The calibration ExampleNet is displayed below:
nux.quantizer.calibrate()
This function executes a calibration model to collect the dynamic range of activations generated from using preprocessed calibration data.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| model | onnx.ModelProto ONNX model |
| calibration_data | Union[Dict[str, np.ndarray], List[Dict[str, np.ndarray]]] Preprocessed calibration data |
Return
Dict[str, Tuple[float, float]] Dynamic range of activations
Result
Calibrating calibration ExampleNet gives the following dynamic range
text
{'input': (1.2729454283544328e-05, 0.9999984502792358), '18': (-0.811184287071228, 1.0816885232925415), '20': (-0.6744376420974731, 0.5646329522132874), '21': (-0.29423975944519043, 0.5646329522132874), 'output': (-0.24178576469421387, 0.20031100511550903)}
nux.quantizer.calibrate_with_random_input()
This function executes a calibration model to collect the dynamic range of activations generated from using randomly generated calibration data.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| model | onnx.ModelProto ONNX model |
Return
Dict[str, Tuple[float, float]] Dynamic range of activations
Result
Calibrating calibration ExampleNet with random calibration gives the follwing dynamic range
text
{'input': (2.170155084968428e-06, 0.9999873042106628), '18': (-1.1680195331573486, 1.125024437904358), '20': (-0.6748880743980408, 0.6123914122581482), '21': (-0.44649842381477356, 0.6123914122581482), 'output': (-0.2456839233636856, 0.39172685146331787)}
Quantization
nux.quantizer.quantize()
Quantization
import nux
optimized_model = ...
input_tensors = ...
dynamic_ranges = ...
quantized_model = nux.quantizer.quantize(optimized_model, input_tensors, dynamic_ranges)
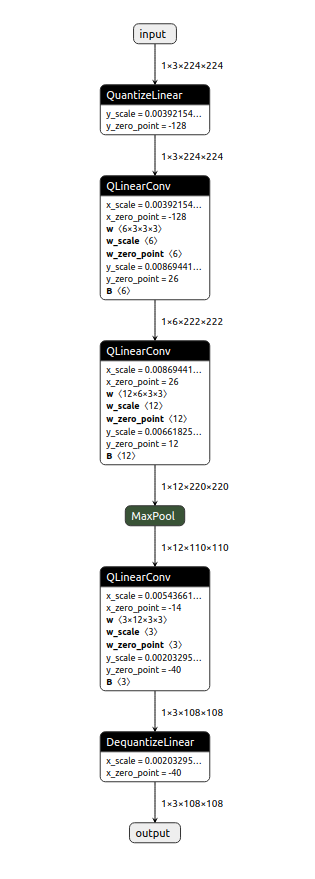
This function quantizes the optimized ONNX model (obtained via graph optimization) with the dynamic range collected by calibration.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| model | onnx.ModelProto ONNX model |
| input_tensors | List[str] Names of the input tensors of the ONNX model |
| dynamic_ranges | Dict[str, Tuple[float, float]] Dynamic range of activations |
Return
onnx.ModelProto static per-channel 8-bit quantized model
Result
The quantized ExampleNet is displayed below:
Nux Python API
The Python API can be accessed in the link below Python API
Nux C/C++ API
create_nux()
Create a Nux handle
#include "nux.h"
nux_handle_t nux;
nux_error_t err = create_nux(&nux);
This API creates a nux handle for subsequent activities.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| nux | Mutable pointer to receive a created Nux handle |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, nux_error_t_nux_creation_failed otherwise.
destroy_nux()
Destroy a Nux handle
#include "nux.h"
destroy_nux(nux);
This API destroys a nux handle.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| nux | Nux handle to be destroyed. It must not be NULL. |
nux_create_sync_model()
Create a synchronous model
#include "nux.h"
nux_sync_model_t sync_model;
nux_error_t err = nux_create_sync_model(nux,
(unsigned char*)buffer,
model_size,
&sync_model);
Generates a synchronous model able to execute a compiled ENF binary. The synchronous model provides an API to execute per-batch inference tasks.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| nux | Mutable pointer to specify Nux handle |
| buffer | Byte buffer containing ENF binary (i.e., model to be used in an inference task) |
| model_size | Byte length of buffer |
| sync_model | Mutable pointer to receive the handle of a created synchronous model |
The corresponding Python API does not require the above parameters. Instead,
it directly takes an enf file path.
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, or nux_error_t_nux_creation_failed otherwise.
destroy_sync_model()
Destroy a synchronous model
#include "nux.h"
destroy_sync_model(sync_model);
Destroys an unneeded synchronous model handle.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sync_model | Synchronous model to be destroyed, and it must not be NULL. |
model_count_inputs()
Get the number of input tensors
#include "nux.h"
nux_sync_model_t sync_model;
...
int nInputs = model_count_inputs(sync_model);
Return the number of input tensors of a given sync model.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sync_model | Synchronous model handle. |
Return
The number of input tensors for the given model.
model_count_outputs()
Get the number of output tensors
#include "nux.h"
nux_sync_model_t sync_model;
...
int nOutputs = model_count_outputs(sync_model);
Return the number of output tensors of a given sync model.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sync_model | Synchronous model handle. |
Return
The number of output tensors for the given model.
model_input_tensor()
Get an input tensor handle for a synchronous model
#include "nux.h"
nux_sync_model_t sync_model;
nux_tensor_t tensor;
int index;
...
nux_error_t err = model_input_tensor(sync_model, index, &tensor);
Get the handle of a specified input tensor from a given sync model.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sync_model | Synchronous model handle. |
| index | Input tensor index. |
| tensor[out] | Mutable pointer to receive the handle of a specified input tensor. |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, or nux_error_t_nux_creation_failed otherwise.
model_output_tensor()
Get an output tensor handle for a synchronous model
#include "nux.h"
nux_sync_model_t sync_model;
nux_tensor_t tensor;
int index;
...
nux_error_t err = model_output_tensor(sync_model, index, &tensor);
Get the handle of a specified output tensor from a given sync model.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sync_model | Synchronous model handle. |
| index | Output tensor index. |
| tensor[out] | Mutable pointer to receive the handle of a specified output tensor. |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, or nux_error_t_nux_creation_failed otherwise.
model_run()
Execute a synchronous model
#include "nux.h"
nux_sync_model_t sync_model;
...
nux_error_t err = model_run(sync_model);
Run a single inference task
Before calling this function, the input tensors must be filled with appropriate data.
Please refer to model_input_tensor and tensor_set_buffer
to learn how to fill input tensors with data.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| sync_model | Synchronous model handle. |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, or nux_error_t_nux_creation_failed otherwise.
tensor_set_buffer()
Copy data to an input tensor
#include "nux.h"
nux_tensor_t inputTensor;
void* buffer;
int buf_size;
...
nux_error_t err = tensor_set_buffer(inputTensor, buffer, buf_size);
To execute model_run, the input tensors must be filled with the necessary data.
This function copies the data into the data buffer of a specified input tensor.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| inputTensor | The tensor handle to copy data from |
| buffer | Pointer to the data buffer. |
| buf_size | Byte length of buffer |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, nux_error_t_invalid_buffer if the buffer is invalid.
tensor_get_buffer()
Copy data from an output tensor
#include "nux.h"
nux_tensor_t outputTensor;
...
nux_buffer_t buffer;
nux_buffer_len_t buf_size;
nux_error_t err = tensor_get_buffer(outputTensor, &buffer, &buf_size);
Get a pointer to the data buffer of a given tensor.
Once model_run is called, the inference result will be written into output tensors.
This function returns a pointer to the data buffer of a specified output tensor.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| outputTensor | The output tensor to get a pointer to the corresponding data buffer |
| buffer | Mutable pointer to receive the pointer to the data buffer |
| buf_size[out] | Byte length of buffer |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful.
nux_create_task_model()
Create a task model
#include "nux.h"
void *buffer;
int max_batch;
int model_size;
nux_handle_t nux;
nux_task_model_t task_model;
nux_error_t err = nux_create_task_model(nux,
(unsigned char*)buffer,
model_size,
max_batch,
output_callback,
error_callback,
finish_callback,
&task_model);
The signatures of the above callback functions should be:
void output_cb(nux_request_id_t id,
nux_output_index_t out_id,
nux_buffer_t buf,
nux_buffer_len_t buf_len) {
// fill your logic
}
void my_error_cb(nux_request_id_t id, nux_error_t err) {
// fill your logic
}
void my_finish_cb(nux_request_id_t id) {
// fill your logic
}
Create an instance of a task model.
This function allows users to run multiple inference tasks asynchronously and simultaneously.
When each task is completed or failed, corresponding callback functions will be called
with nux_request_id_t, an identifier of a task request.
See also task_execute() for more details.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| nux | Nux handle. |
| buffer | Byte buffer containing ENF binary. |
| model_size | Byte length of buffer |
| max_batch | Number of concurrent running tasks (can be limited according to internal configurations and HW capacity) |
| output_callback | Callback function invoked when a task is completed, called per output tensor |
| error_callback | Callback function invoked when a task fails |
| finish_callback | Callback function called after the output_callback has been called for all output tensors |
| task_model | Mutable pointer to receive the handle of a created task model. |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, nux_error_t_nux_creation_failed otherwise.
task_model_get_task()
Get a task from a task model
#include "nux.h"
nux_task_model_t task_model;
...
nux_task_t task;
nux_error_t err = task_model_get_task(task_model, &task);
Retrieve a task handle from a specified task model.
If there is no available task in a given task model, the function will block further operations until a new task is available.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| task_model | Handle of a task model. |
| task | Mutable pointer to receive the handle of a created task. |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, nux_error_t_model_execution_failed otherwise.
task_model_try_get_task()
Get a task from a task model (Non-blocking)
#include "nux.h"
nux_task_model_t task_model;
...
nux_task_t task;
nux_error_t err = task_model_try_get_task(task_model, &task);
Get a task handle from the specified task model without blocking operations.
The non-blocking version of task_model_get_task.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| task_model | Handle of a task model. |
| task | Mutable pointer to receive the handle of a created task. |
Return
An available task in a given task model, nux_error_t_get_task_failed otherwise.
task_input()
Get a task input tensor handle
#include "nux.h"
nux_task_t task;
...
nux_buffer_t buffer = task_input(task, index);
Return a mutable pointer to the buffer of the specified input tensor.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| task | Task handle |
| index | Index of the input tensor. |
Return
A mutable pointer to the data buffer of the given input tensor.
task_input_size()
Get the size of an input tensor
#include "nux.h"
nux_task_t task;
...
nux_buffer_len_t length = task_input_size(task, 0);
Return the buffer length in bytes of the specified input tensor.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| task | Task handle |
| index | Index of the input tensor. |
Return
The size of the specified input tensor.
task_execute()
Run a task model
#include "nux.h"
nux_task_t task;
nux_request_id_t request_id;
...
nux_error_t err = task_execute(task, request_id);
Request an asynchronous inference task.
This function submits a request for a specific inference task.
Once the task is completed, the output_callback function is passed to nux_create_task_model function,
which is called with a distinct output index per output tensor.
The finish_callback function will be also called
after output_callback function is called for all output tensors.
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| task | Task handle obtained from calling task_model_get_task or task_model_try_get_task. |
| request_id | An positive integer to distinguish task requests. Only passed to callback functions, task_execute has no dependency on request_id. |
Return
nux_error_t_success if successful, nux_error_t_model_execution_failed otherwise.
destroy_task_model()
Destroy a task model
#include "nux.h"
destroy_task_model(task_model);
Destroy the task model and release its resources.
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| task_model | Task model to be destroyed. |
task_model_is_all_task_done()
Check whether all tasks are done
#include "nux.h"
nux_task_model_t task_model;
...
bool ck = task_model_is_all_task_done(task_model);
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| task_model | Task model handle. |
Return
true if there's no running tasks, or false otherwise.
Operators Accelerated on Furiosa NPU
The following 28 operators of ONNX operators are accelerated on Furiosa NPU.
- Add
- AveragePool
- Clip
- Concat
- Conv
- ConvTranspose
- DepthToSpace
- Exp
- Expand
- Flatten
- Gemm
- LpNormalization (when p = 2)
- MatMul
- MaxPool
- Mean
- Mul
- Pad
- ReduceL2
- ReduceSum
- Relu
- Reshape
- Sigmoid
- Slice
- Softmax
- Softplus
- Split
- Transpose
- Unsqueeze
