Release Notes - 0.8.0
Furiosa SDK 0.8.0 is a major release, including many performance enhancements, additional functions, and bug fixes. 0.8.0 also includes the serving framework, a core tool of user application development, as well as major improvements to the Model Zoo.
Package Name |
Version |
|---|---|
NPU Driver |
1.4.0 |
NPU Firmware Tools |
1.2.0 |
NPU Firmware Image |
1.2.0 |
HAL (Hardware Abstraction Layer) |
0.9.0 |
Furiosa Compiler |
0.8.0 |
Python SDK (furiosa-runtime, furiosa-server, furiosa-serving, furiosa-quantizer, ..) |
0.8.0 |
NPU Device Plugin |
0.10.1 |
NPU Feature Discovery |
0.2.0 |
NPU Management CLI (furiosactl) |
0.10.0 |
Installing the latest SDK
If you are using APT repository, the upgrade process is simpler.
apt-get update && apt-get upgrade
If you wish to designate a specific package for upgrade, execute as below: You can find more details about APT repository setup at Driver, Firmware, and Runtime Installation.
apt-get update && \ apt-get install -y furiosa-driver-pdma furiosa-libhal-warboy furiosa-libnux furiosactl
You can upgrade firmware as follows:
apt-get update && \ apt-get install -y furiosa-firmware-tools furiosa-firmware-image
You can upgrade Python package as follows:
pip install --upgrade furiosa-sdk
Major changes
Improvements to serving framework API
The furiosa-serving is a FastAPI-based serving framework. With the furiosa-serving, users can quickly develop Python-based high performance web service applications that utilize NPUs. The 0.8.0 release includes the following major updates.
Session pool that enables model serving with multiple NPUs
Session pools improve significantly throughput of model APIs by using multiple NPUs. If large inputs can be divided into a number of small inputs, this improvement can be used to reduce the latency of serving applications.
model: NPUServeModel = synchronous(serve.model("nux"))(
"MNIST",
location="./assets/models/MNISTnet_uint8_quant_without_softmax.tflite",
# Specify multiple devices
npu_device="npu0pe0,npu0pe1,npu1pe0"
worker_num=4,
)
Shift from thread-based to asyncio-based NPU query processing
Small and frequent NPU inference queries may now be processed with lower latency. As shown in the example below, applications requiring multiple NPU inferences in a single API query can be processed with better performance.
async def inference(self, tensors: List[np.ndarray]) -> List[np.ndarray]:
# The following code runs multiple inferences at the same time and wait until all requests are completed.
return await asyncio.gather(*(self.model.predict(tensor) for tensor in tensors))
Added expanded support for external device & runtime
In complex serving scenarios, additional/external device and runtime programs may be required, in addition to NPU-based Furiosa Runtime. In this release, the framework has been expanded such that external device and runtime may be used. The first external runtime added is OpenVINO.
imagenet: ServeModel = synchronous(serve.model("openvino"))(
'imagenet',
location='./examples/assets/models/image_classification.onnx'
)
Support for S3 cloud storage repository
Set model location as S3 URL.
# Load model from S3 (Auth environment variable for aioboto library required)
densenet: ServeModel = synchronous(serve.model("nux"))(
'imagenet',
location='s3://furiosa/models/93d63f654f0f192cc4ff5691be60fb9379e9d7fd'
)
Support for OpenTelemetry compatible tracing
With the OpenTelemetry Collector function, you can now track the execution time of specific code sections of the serving applications.
To use this function, you can activate trace.get_tracer(), reset the tracer,
activate the tracer.start_as_current_span() function, and designate the section.
from opentelemetry import trace
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
class Application:
async def process(self, image: Image.Image) -> int:
with tracer.start_as_current_span("preprocess"):
input_tensors = self.preprocess(image)
with tracer.start_as_current_span("inference"):
output_tensors = await self.inference(input_tensors)
with tracer.start_as_current_span("postprocess"):
return self.postprocess(output_tensors)
The specification of OpenTelemetry Collector
can be done through the configuration of FURIOSA_SERVING_OTLP_ENDPOINT, as shown below.
The following diagram is an example that visualizes the tracing result with Grafana.
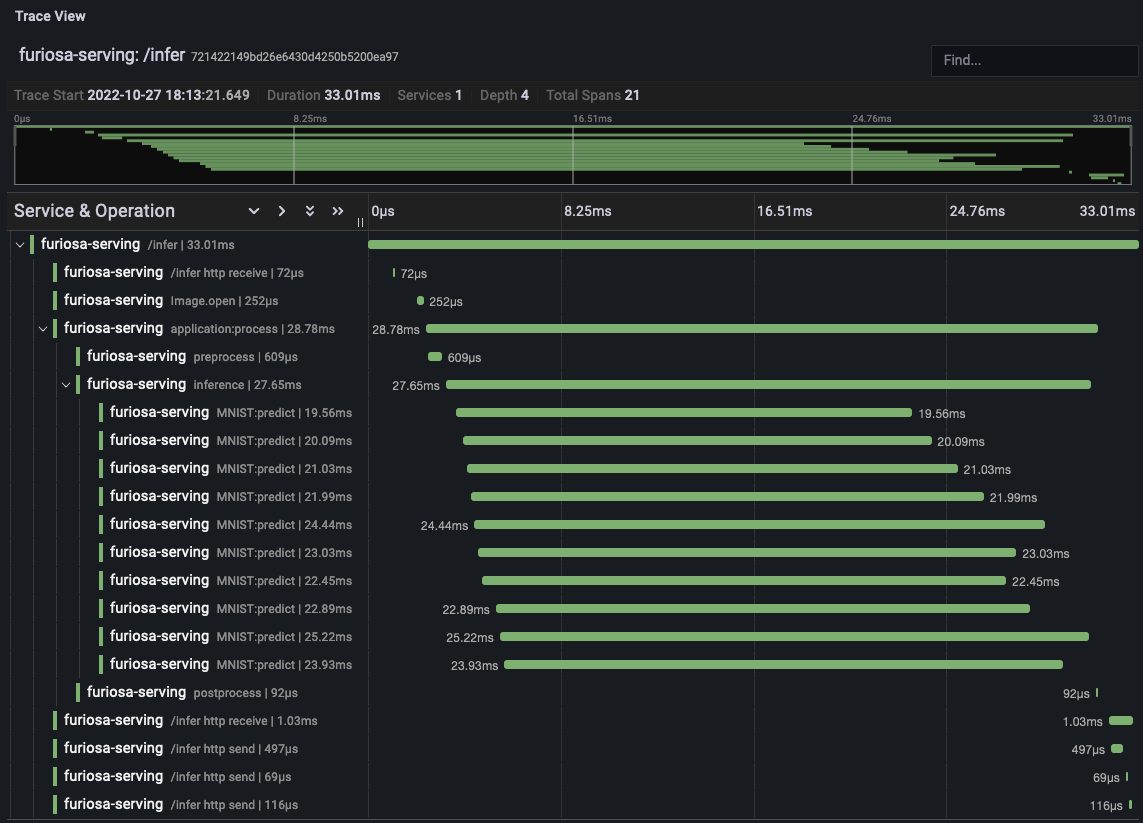
Other major improvements are as follows:
Several inference requests can be executed at once, with serving API now supporting compiler setting
batch_sizeMore threads can share the NPU, with serving API now supporting session option
worker_num
Profiler
You can now analyze the profiler tracing results with Pandas, a data analysis framework. With this function, you can analyze the tracing result data, allowing you to quickly identify bottlenecks and reasons for model performance changes. More detailed instructions can be found at Trace analysis using Pandas DataFrame.
from furiosa.runtime import session, tensor
from furiosa.runtime.profiler import RecordFormat, profile
with profile(format=RecordFormat.PandasDataFrame) as profiler:
with session.create("MNISTnet_uint8_quant_without_softmax.tflite") as sess:
input_shape = sess.input(0)
with profiler.record("record") as record:
for _ in range(0, 2):
sess.run(tensor.rand(input_shape))
df = profiler.get_pandas_dataframe()
print(df[df["name"] == "trace"][["trace_id", "name", "thread.id", "dur"]])
Quantization tool
Model Quantization is a tool that converts pre-trained models to quantized models. This release includes the following major updates.
Accuracy improvement when processing SiLU operator
Improved usability of compiler setting
without_quantizeAccuracy improvement when processing MatMul/Gemm operators
Accuracy improvement when processing Add/Sub/Mul/Div operators
NPU acceleration now added for more auto_pad properties, when processing Conv/ConvTranspose/MaxPool operators
NPU acceleration support for PRelu operator
furiosa-toolkit
The furiosactl command line tool, which has been added to the
furiosa-toolkit 0.10.0 release, includes the following improvements.
The newly added furiosactl ps command allows you to print the OS processes which are occupying the NPU device.
# furiosactl ps
+-----------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------+
| NPU | PID | CMD |
+-----------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------+
| npu0pe0-1 | 132529 | /usr/bin/python3 /usr/local/bin/uvicorn image_classify:app |
+-----------+--------+------------------------------------------------------------+
The furiosactl info command now prints the unique UUID for each device.
$ furiosactl info
+------+--------+--------------------------------------+-----------------+-------+--------+--------------+---------+
| NPU | Name | UUID | Firmware | Temp. | Power | PCI-BDF | PCI-DEV |
+------+--------+--------------------------------------+-----------------+-------+--------+--------------+---------+
| npu0 | warboy | 72212674-61BE-4FCA-A2C9-555E4EE67AB5 | v1.1.0, 12180b0 | 49°C | 3.12 W | 0000:24:00.0 | 235:0 |
+------+--------+--------------------------------------+-----------------+-------+--------+--------------+---------+
| npu1 | warboy | DF80FB54-8190-44BC-B9FB-664FA36C754A | v1.1.0, 12180b0 | 54°C | 2.53 W | 0000:6d:00.0 | 511:0 |
+------+--------+--------------------------------------+-----------------+-------+--------+--------------+---------+
Detailed instructions on installation and usage for furiosactl can be found in furiosa-toolkit.
Model Zoo API improvements, added models, and added native post-processing code
furioa-models is a public Model Zoo project, providing FuriosaAI NPU-optimized models. The 0.8.0 release includes the following major updates.
YOLOv5 Large/Medium models added
Support for YOLOv5l, YOLOv5m, which are SOTA object detection models, have been added.
The total list of available models can be found in
Model List.
Improvements to model class and loading API
The model class has been improved to include pre and post-processing code, while the model loading API has been improved as shown below.
More explanation on model class and the API can be found at Model Object.
Before update
from furiosa.models.vision import MLCommonsResNet50
resnet50 = MLCommonsResNet50()
Updated code
from furiosa.models.vision import ResNet50
resnet50 = ResNet50.load()
Before update
import asyncio
from furiosa.models.nonblocking.vision import MLCommonsResNet50
resnet50: Model = asyncio.run(MLCommonsResNet50())
0.8.0 improvements
import asyncio
from furiosa.models.vision import ResNet50
resnet50: Model = asyncio.run(ResNet50.load_async())
The model post-processing process converts the inference ouput tensor into structural data, which is more accessible for the application. Depending on the model, this may require a longer execution time. The 0.8.0 release includes native post-processing code for ResNet50, SSD-MobileNet, and SSD-ResNet34. Based on internal benchmarks, native post-processing code can reduce latency by up to 70%, depending on the model.
The following is a complete example of ResNet50, utilizing native post-processing code. More information can be found at Pre/Postprocessing.
from furiosa.models.vision import ResNet50 from furiosa.models.vision.resnet50 import NativePostProcessor, preprocess from furiosa.runtime import session model = ResNet50.load() postprocessor = NativePostProcessor(model) with session.create(model) as sess: image = preprocess("tests/assets/cat.jpg") output = sess.run(image).numpy() postprocessor.eval(output)
Other changes and updates can be found at Furiosa Model - 0.8.0 Changelogs.